Exploring Google BigLake: A Game-Changer for Data Management
Written on
Chapter 1: Introduction to Google BigLake
In the realm of data management, we've seen the evolution from traditional Data Warehouses and Data Lakes to the emerging concept of Data Lakehouses, with Google now introducing BigLake. This powerful tool aims to enhance integration and functionality across its platform.
Definition
Google is striving to improve the connection between Data Lakes (Cloud Storage) and Data Warehouses (BigQuery). This approach supports the development of Data Meshes and a data-centric organization. BigLake serves as a solution to unify these services, facilitating better integration and performance. As Google outlines:
> BigLake is built on years of investment in BigQuery, acting as a storage engine that allows organizations to merge data warehouses and lakes while enabling fine-grained access control and accelerating query performance across multi-cloud storage and open formats.
How It Functions
To begin utilizing BigLake, organizations must first create an "External data source" in BigQuery.
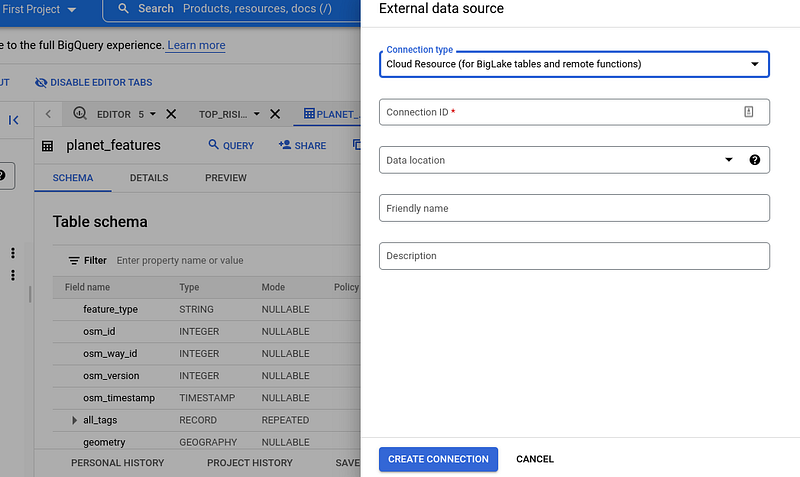
Once established, users can select from various sources, such as Cloud SQL or data from AWS and Azure. It's remarkable how data analysis can span multiple cloud platforms.
BigLake accesses data within Google Cloud Storage via a connection resource, which can link to individual tables or groups of tables in a project.
Step 2: Table Creation
After establishing the connection, you can create tables that utilize Cloud Storage along with the external data source connection.
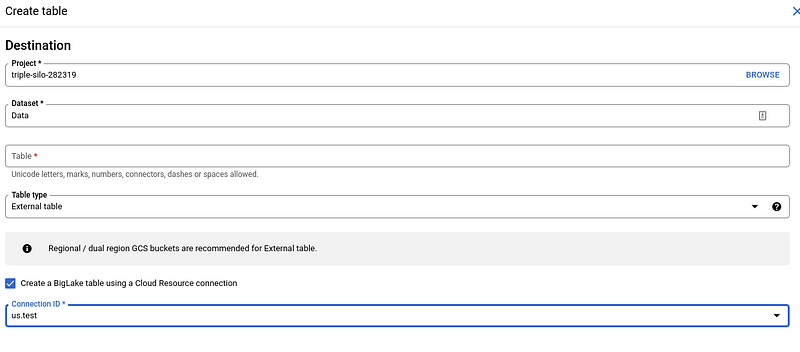
For comprehensive guidance on setting up access control policies, be sure to consult the official documentation.
Benefits
The implementation of BigLake brings several advantages to organizations in terms of data integration and analysis:
Benefit 1: Enhanced Security and Governance Controls
BigLake streamlines user access by eliminating the need for file-level permissions. Instead, you can apply security policies at the table, row, and column levels on object store tables, akin to existing BigQuery tables.
Benefit 2: Performance and Scalability
Leveraging the power of Google’s BigQuery, users can efficiently query tables on Google Cloud, AWS, and Azure, ensuring robust performance and scalability.
Benefit 3: Compatibility with Open Formats and Simplified Data Management
With BigLake, data remains in its original location, minimizing the need for data duplication and reducing discrepancies. It supports popular open data formats like Parquet, Avro, ORC, CSV, and JSON.
Summary
Data Lakehouses and the concept of data meshes are well-understood in the industry. With the launch of BigLake, Google enhances user experience and accessibility to diverse data sources.
Sources and Further Readings
[1] Google, BigLake (2022)
[2] Google, Create and manage BigLake tables (2022)
Chapter 2: Visual Insights into BigLake
Explore a quick overview of BigLake's functionalities and advantages in this concise video.
Learn how to set up your first Cloud BigLake in GCP through this informative tutorial.