Understanding Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
Written on
Chapter 1: What Are Atoms?
Atoms represent the fundamental components of matter, encompassing everything that exists in the universe.
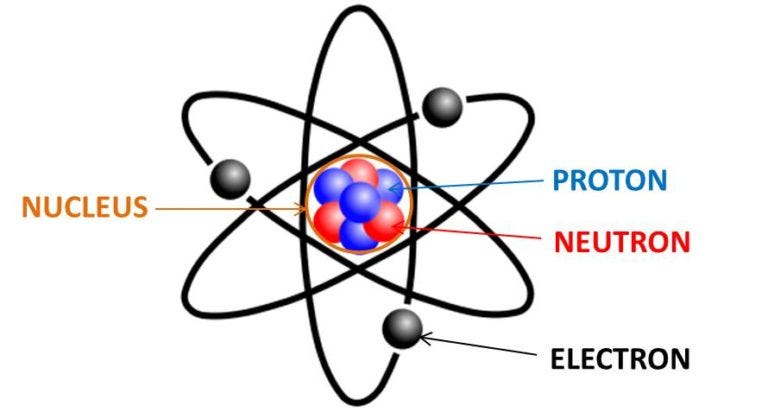
The structure of an atom includes a nucleus at its core, housing protons and neutrons, while electrons orbit around this nucleus in areas known as electron shells.
Protons carry a positive electrical charge, while neutrons are neutral, and electrons possess a negative charge. This structure can be likened to a battery, where protons and electrons create a balance of electrical charges.
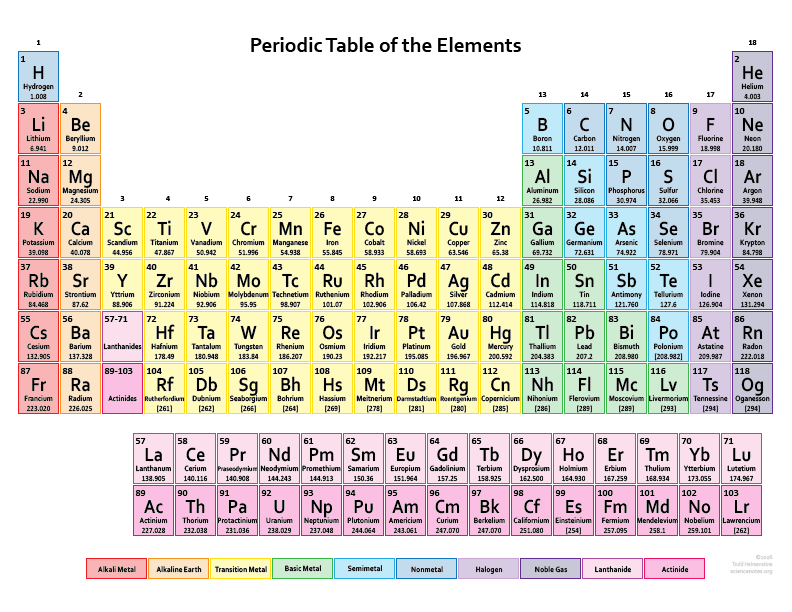
Each unique atom constitutes a pure substance referred to as an element. Examples of these elements include oxygen, lead, and gold. Remarkably, a single gold necklace consists of countless individual gold atoms!
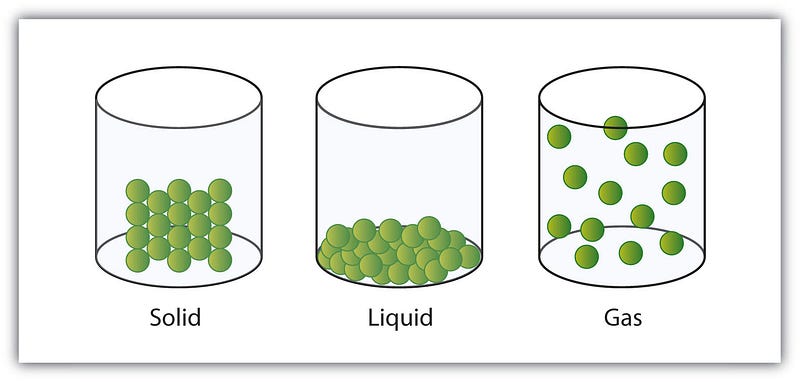
Atoms are not prone to breaking down into smaller units. They can exist independently or bond together, forming what are known as bonded atoms. These bonded atoms can create various substances. In some cases, they may cluster so closely that their movement is severely restricted, akin to being trapped in a cramped elevator, resulting in the formation of solids like rocks.

When atoms have more space to move, they transition into liquids. Envision how much easier it would be to move if the elevator were less crowded, with only you and a couple of friends.
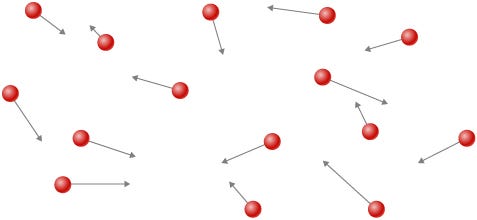
Atoms that enjoy unrestricted movement give rise to gases, which lack a fixed shape. Imagine stepping out of an elevator into a spacious lobby; you and your friends might separate and explore due to the ample space available. This scenario mirrors the behavior of gas molecules.
The first video, "What Is An Atom And How Do We Know?", offers insights into the atomic structure and its significance in matter.
The second video, "What is an Atom - Basics for Kids," provides a foundational understanding of atoms, making the concept accessible for younger audiences.
Summary
Atoms serve as the tiniest building blocks of matter, forming everything that surrounds us. At the heart of each atom lies a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons, with electrons orbiting around it. Atoms can bond together to create solids, liquids, or gases, illustrating the diversity of matter in our world.