The Long-Term Healthcare Costs of COVID-19 Infections
Written on
Understanding the Healthcare Impact of COVID-19
A COVID-19 infection results in an average increase of nine additional medical visits annually.

As of February 2024, the toll of COVID-19 had reached 1.2 million lives in the United States — a number surpassing the casualties of World War II, the 1918 "Spanish" flu, the Civil War, and the entire AIDS epidemic. However, this narrative focuses not on those lost but on the survivors. Given that nearly everyone in the U.S. has been infected, this discussion pertains to the collective experience and the ongoing repercussions of the virus on national health.
This examination does not center on long COVID — a syndrome that remains vaguely defined and for which I've previously noted the absence of a clear case definition. Instead, I aim to highlight the extent of healthcare services that COVID-19 has compelled us to use — both during and after the infection.
Section 1.1 The Consumption of Healthcare Services
COVID-19 infections drive individuals to seek various healthcare services — including doctor visits, emergency room (ER) visits, and hospital admissions — particularly during the acute phase. However, what happens once that phase concludes? Emerging data indicates that COVID-19 effectively resets the healthcare consumption baseline — leading to increased healthcare usage not just in the short term but extending for weeks, months, and even years afterward.
The challenge in the U.S. is that without a cohesive healthcare system, it becomes difficult to accurately assess healthcare usage before and after a COVID-19 infection. The one notable exception is the Veterans Health Administration (VA), which represents a fully socialized healthcare model in the U.S.
A significant study conducted by Paul Hebert and colleagues at VA Puget Sound, published in JAMA Network Open, sheds light on how much healthcare is consumed before and after a COVID-19 infection.

Source: Hebert et al. JAMA Network Open 2024.
Analyzing the Study's Methodology
Before sharing the findings, it’s important to acknowledge the complexities of this study. Patients with pre-existing health conditions tend to use more healthcare services and are at a greater risk of COVID-19, necessitating a robust control group for comparison.
Researchers identified 202,803 Veterans who had contracted COVID-19 and matched them with an equal number of uninfected Veterans, ensuring that variables such as sex, state of residence, immunosuppressive medication use, and vaccination status were consistent. They further matched participants based on a propensity score reflecting the likelihood of COVID-19 infection, derived from 37 different factors, including demographics, comorbidities, and healthcare utilization.
Ultimately, the study created a “digital twin” approach, where each infected participant was paired with a closely matched uninfected counterpart. This allowed researchers to determine the transition point for the control group based on when their counterpart became infected.
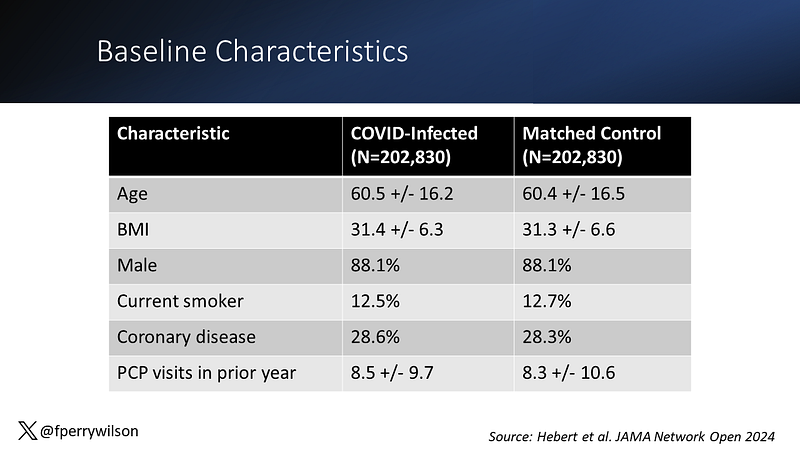
While not a randomized trial, the groups were well matched in terms of age, BMI, and smoking status, enhancing the validity of the results.
Section 1.2 Observing Healthcare Utilization Trends
Prior to infection, both groups exhibited similar, low levels of emergency care usage. However, post-infection, the COVID-19 group displayed a significant spike in ER visits, as expected. Notably, while ER visit rates decreased relatively quickly, they remained slightly elevated compared to the control group.
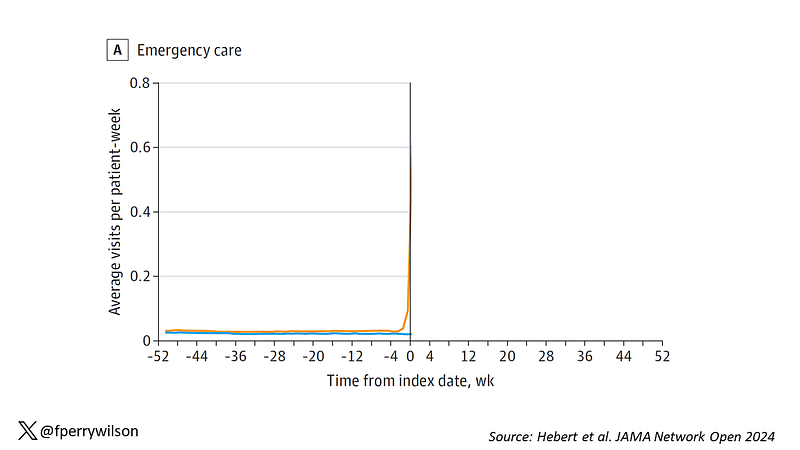
Source: Hebert et al. JAMA Network Open 2024.
The study becomes particularly intriguing when examining primary care visits. Initially, both groups had similar utilization rates. However, following infection, there was a substantial increase in the COVID group, which persisted even 52 weeks later, translating to roughly two additional primary care visits annually for each COVID-19 infection.
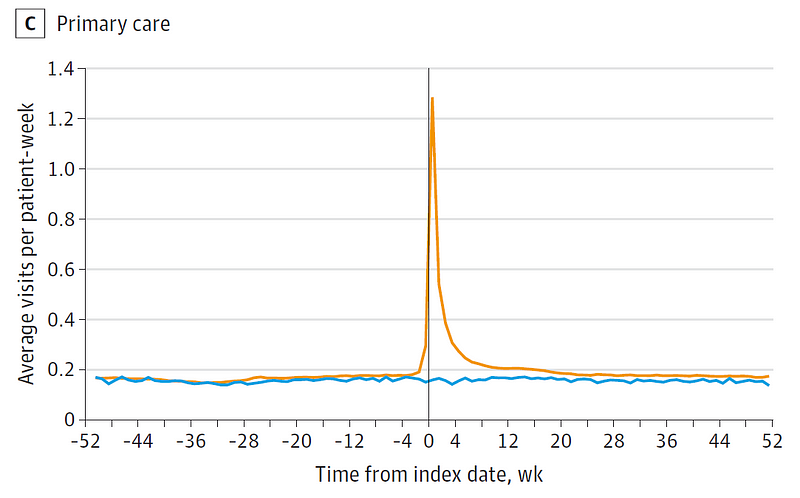
Source: Hebert et al. JAMA Network Open 2024.
Interestingly, mental health service usage also spiked at the time of infection, suggesting profound implications on mental health as well.
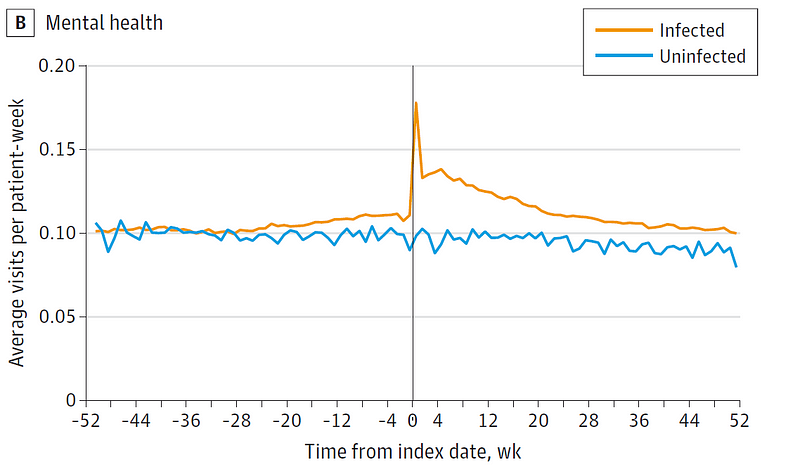
Source: Hebert et al. JAMA Network Open 2024.
The study concluded that on average, COVID-19 patients had approximately nine additional healthcare visits in the year following their infection compared to well-matched controls. This significant increase in healthcare utilization raises concerns, as resources are finite.
Addressing the Healthcare Burden
However, subgroup analyses revealed that the rise in healthcare consumption post-infection was less pronounced among younger individuals and during later pandemic waves. Additionally, vaccinated individuals experienced a smaller increase in healthcare utilization, highlighting an area where interventions can be made.
This research underscores the often overlooked consequences of the pandemic — factors that are challenging to quantify yet are felt in everyday medical practice. Physicians are now busier and facing greater stress, managing patients who are increasingly unwell. As we navigate the aftermath of this global crisis, we must confront the new challenges that have emerged.
Chapter 2 The Lasting Impact of COVID-19 on Healthcare Systems
The first video, "Measuring the Cost of COVID in Doctor's Visits," discusses the implications of increased healthcare visits due to COVID-19.
The second video, "COVID-19 Changes Medical Practice, Maybe Forever," explores the lasting changes to healthcare practices stemming from the pandemic.