Mapping the Human Brain: A $500 Million Initiative
Written on
Chapter 1: The Brain Initiative 2.0
The Brain Science Project has unveiled the “Cell Atlas Network Project,” a groundbreaking effort to create a detailed human brain cell atlas, akin to the monumental Human Genome Project. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) has announced two pioneering initiatives under the Brain Science Initiative: the “Brain Science Project’s Cell Atlas Network Project” (BICAN) and the “Centre for Access Equipment for Precise Brain Cells.”

BICAN will be allocated $500 million over the next five years, with the ambition of providing the most comprehensive mapping of brain cells to date. This initiative is expected to significantly enhance our comprehension of brain cell types and the tools necessary to study them, advancing our understanding of the human brain's intricate workings.
This new endeavor is part of a broader context; the original Brain Initiative was launched by former President Barack Obama in 2013 and has evolved over nine years.

Initially, the Brain Science Project focused on developing tools. The project later introduced the “Brain Cell Census Network Project,” yielding numerous publications by 2021. These studies aggregated data on genetic features, morphology, locations, and electrical activities of millions of cells, identifying over 100 distinct cell types in the primary motor cortex of mice, marmosets, and humans.
Hundreds of researchers involved in the Brain Cell Census Network project are currently working to complete cell mappings across the entire mouse brain. Once finalized, this resource will be accessible to the neuroscience community at large.
The confidence to propose an ambitious challenge—mapping the most comprehensive human brain cell atlas—comes after years of investment and preliminary research.

Scientists assert that the $500 million BICAN initiative could revolutionize our understanding of human brain functionality and the impact of diseases on this complex organ. Zeng Hongkui, director of the Allen Institute for Brain Science, which received a third of BICAN's funding, emphasizes that BICAN will follow a methodology similar to the brain cell census network project, but on a more extensive scale.
Given that the human brain comprises around 200 billion cells—1,000 times larger than that of a mouse—the challenges presented by this endeavor are substantial.
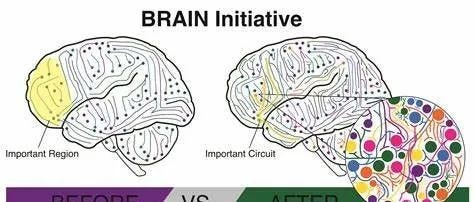
Zeng believes that the implications of this work are profound, potentially serving as a reference point for neuroscience similar to the Human Genome Project. Joseph Ecker from the Salk Institute for Biological Studies, leading the BICAN epigenetics research, expresses ambitions to explore genetic changes that occur without altering DNA, covering human development from childhood through aging.
The NIH expresses strong support for BICAN's goals, with John Ngai, director of the NIH’s BRAIN program, stating that this initiative will revolutionize neuroscience research for generations to come.
The first video titled "Is There a Limit To Our Brains? Can We Understand Reality?" discusses the boundaries of human cognition and our quest to comprehend the complexities of reality.
Ngai hopes to examine several hundred human brains in detail, although the specifics of sampling and coverage are still under discussion. An additional $36 million funding over three years will support the Center for Precision Brain Cell Access Devices, which will leverage new census data and cutting-edge technology to develop tools for researchers.
These tools will include viral vectors and lipid nanoparticles designed to target and genetically modify specific brain cell types.
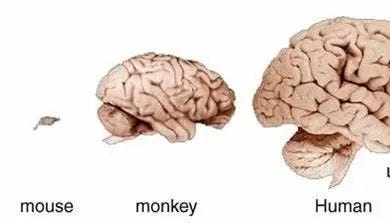
With these advancements, scientists will delve into specific brain cells and neural circuits in various model systems, enhancing our understanding of cell functions and paving the way for disease treatments. This toolkit promises to facilitate in-depth studies of neural circuits during complex behaviors, establishing a foundation for future precision gene therapies.
In addition to the BICAN initiative, the NIH is planning to fund the Cross-Scale Connectivity Networks Project (BRAIN CONNECTS), which focuses on tracing the wiring diagrams in mammalian brains, with a projected $30 million grant over five years expected to start early next year. Collectively, these projects have the potential to transform neuroscience research, unraveling fundamental principles governing behavioral circuits and offering new strategies for treating brain disorders.
To date, the NIH has invested a total of $2.5 billion in the BRAIN initiative, with expectations for this figure to reach $5.2 billion by the end of 2026.

Chapter 2: Advancements in Brain Research
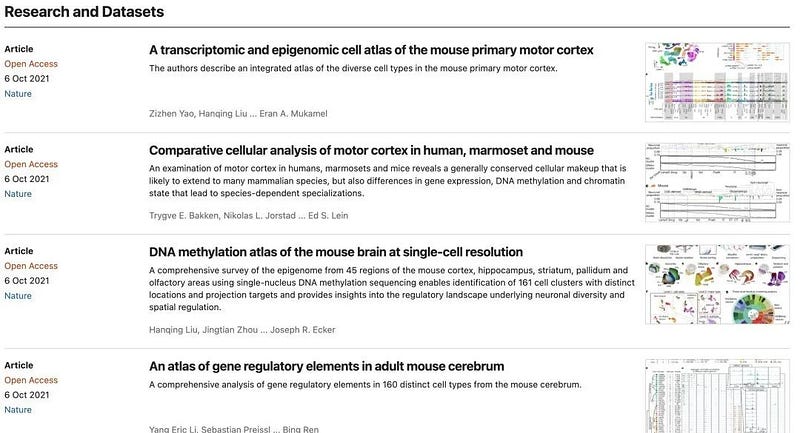
In 2017, to further investigate brain complexities, the NIH launched the “Brain Cell Census Network Project” (BICCN), which has been pushing the boundaries of innovative neurotechnology.
The objective of this project is to identify and catalog various cell types within human, monkey, and mouse brains comprehensively. After three years of progress, significant breakthroughs in this field were published in October 2021, with Nature releasing 16 papers on the subject.
Researchers have effectively mapped cell types in the primary motor cortex of mammals at the molecular level, signifying a key milestone in this ambitious project. The primary motor cortex was selected for its structural similarities across all mammals, underscoring the similarities in movement control despite the differences among human, monkey, and mouse brains.

This area of the brain is critical, as it integrates sensory and motor information while generating complex cognitive functions. Below, transcriptome data clustered by brain cell type in human, marmoset, and mouse brains illustrates these findings.

The significance of these results cannot be overstated; the resulting brain map will assist in understanding various brain disorders, particularly those affecting motor neurons, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Moreover, major American tech firms, including Google, have invested heavily in brain research. In 2019, Google successfully created the first 3D model of neurons in the Drosophila brain, employing the Flood-Filling Network algorithm and TPU chips. The researchers sliced the fruit fly brain into thousands of ultra-thin sections, generating over 40 trillion pixel images of the entire brain.
In 2020, Google unveiled the Drosophila “half-brain” connectome, illustrating 25,000 neurons, approximately one-third of the fly's brain volume. The latest “H01” dataset released in 2021 represents a 1.4 PB sample rendering of human brain tissue, marking the first large-scale study of “synaptic connectivity” across various cell types in the human cerebral cortex.
As we continue to explore the complexities of the human brain, the ongoing advancements in brain research are expected to unveil more of its mysteries and significantly contribute to the development of artificial general intelligence (AGI).
The second video titled "Chapter 8 Homework Solutions MyMathLab" provides insights into the educational tools and methodologies related to brain research and data analysis.
References: