The Science Behind Rainbows: Understanding Their Physics
Written on
Chapter 1: Introduction to Rainbow Physics
The phenomenon of rainbows is rooted in straightforward physics. Essentially, the location of a rainbow is determined by a single raindrop. To understand this, one must apply Snell’s law of refraction along with the law of reflection. The remaining concepts are based on Euclidean geometry. Despite its simplicity, the physics of rainbows can yield unexpected insights. For example, we can demonstrate that rainbows are predominantly a terrestrial occurrence. Saturn's moon Titan, which experiences cloud cover and ammonia rainfall, does not exhibit rainbows. This article aims to clarify this assertion. Initially, I crafted this topic as a practical exercise for my students, focusing on the interactive plotting of geometric constructions using matplotlib.
So, here’s the challenge: Imagine you’re outside with the sun directly behind you, and in front of you, it's raining. You can see your shadow. To spot a rainbow, at what angle must you tilt your head? Moreover, under what circumstances does the rainbow become visible? Ideally, use matplotlib instead of traditional pencil and paper to hone your skills within the Python scientific ecosystem.
Video Description: This video explains the formation of rainbows, detailing how light interacts with water droplets to create this stunning optical phenomenon.
Chapter 2: Setting Up the Geometry
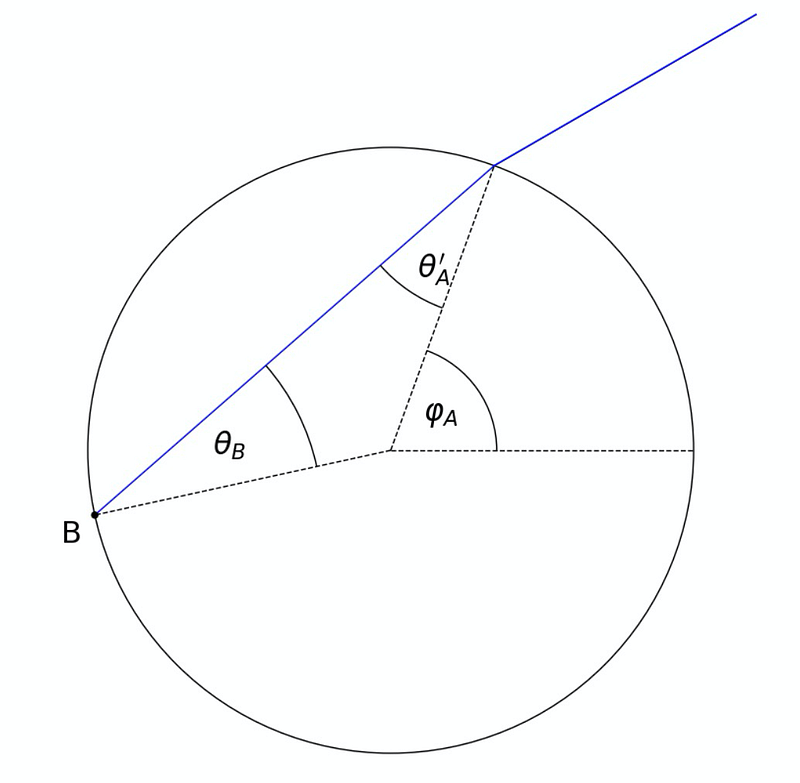
Let’s begin by graphing the overall scenario and establishing our coordinate system. We’ll position a spherical raindrop at the center, with the x-axis running horizontally and the sun positioned at an angle above the horizon. For the moment, we will focus on a single ray of light. Assume this ray strikes the droplet at a polar angle:
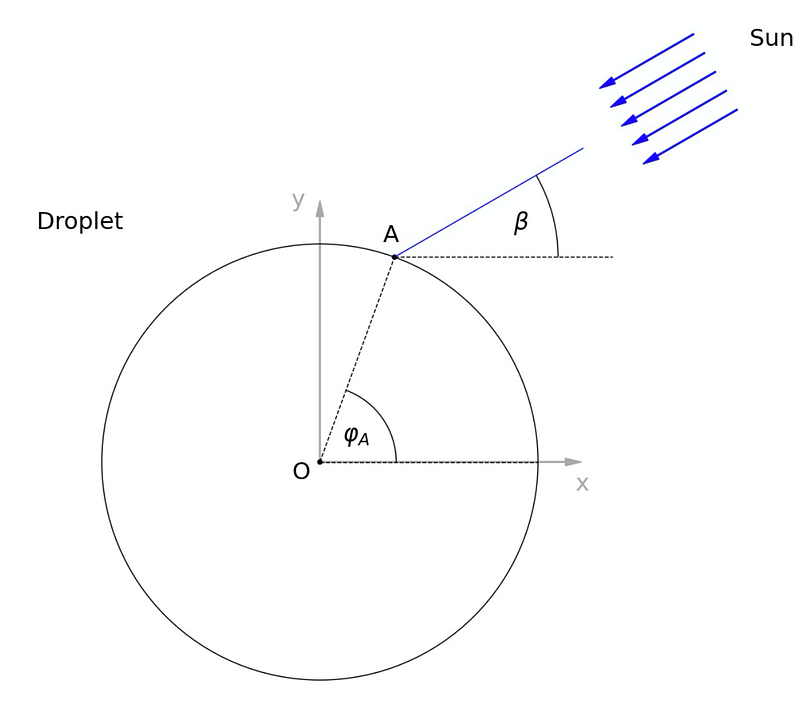
Section 2.1: Analyzing the Light Path
By zooming in, we can examine the behavior of the light ray:
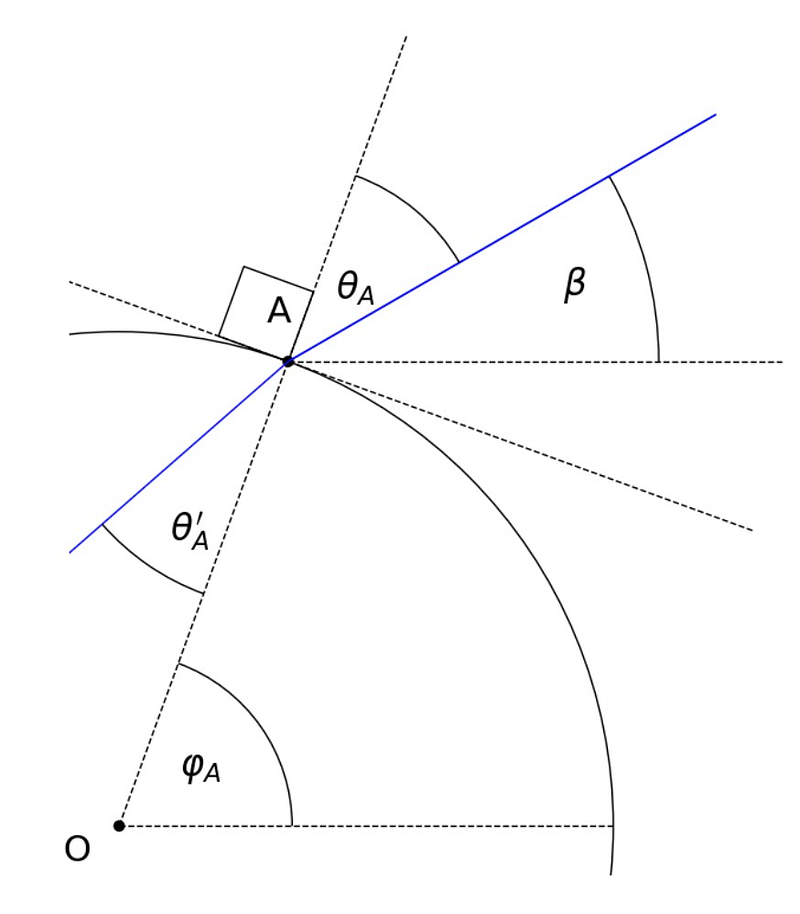
When the sunlight encounters the droplet at a specific angle, it refracts, altering its trajectory as described by Snell’s law:
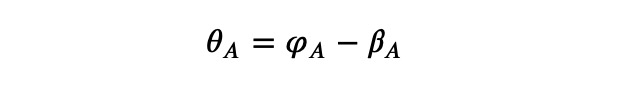
Here, the various angles are measured from the normal line. The refractive indices of the involved materials are critical in understanding this process. Once the light travels through the raindrop and impacts the opposite side, its journey continues:
Section 2.2: Reflection and Exit
As the light ray reflects off the inside of the droplet:
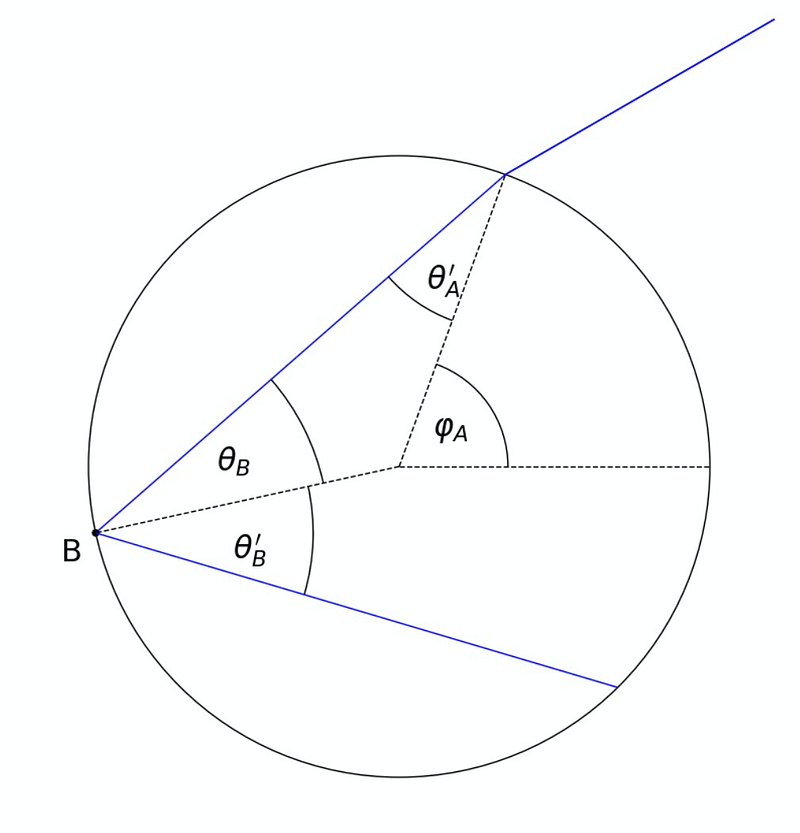
The law of reflection indicates that the angle relative to the normal remains unchanged:
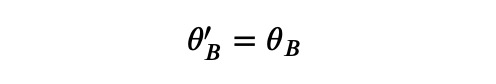
After passing through the droplet, the light undergoes refraction once more as it exits:
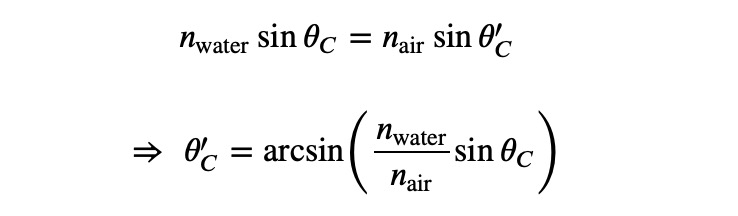
Video Description: This video delves into the physics of rainbows, explaining how light behaves when it strikes raindrops, resulting in the beautiful spectrum we see.
Section 2.3: Practical Implications
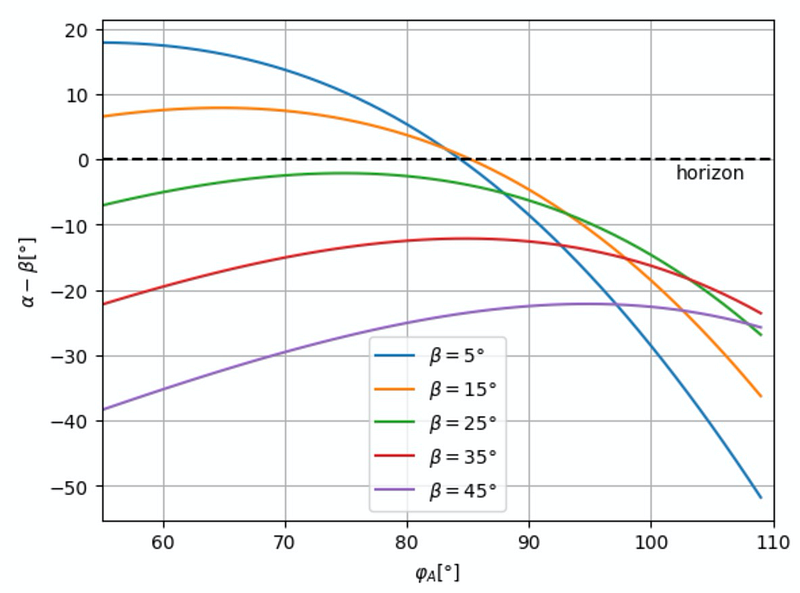
Now, let's answer the question: at what angle must one look to see the rainbow when gazing at the tip of one's shadow? The following visual representation illustrates this scenario:
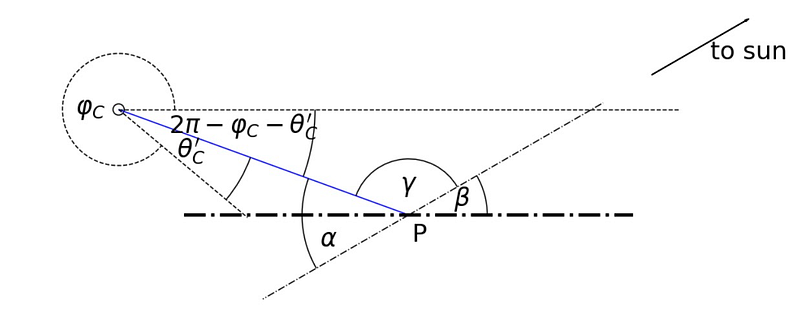
In this setup, we can derive the angles involved:
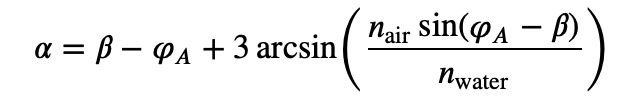
Conclusion: Rainbows Beyond Earth
To gain a deeper understanding, we can graph the light paths for different sun elevations. For instance, if the sun is at 20°, we can observe:
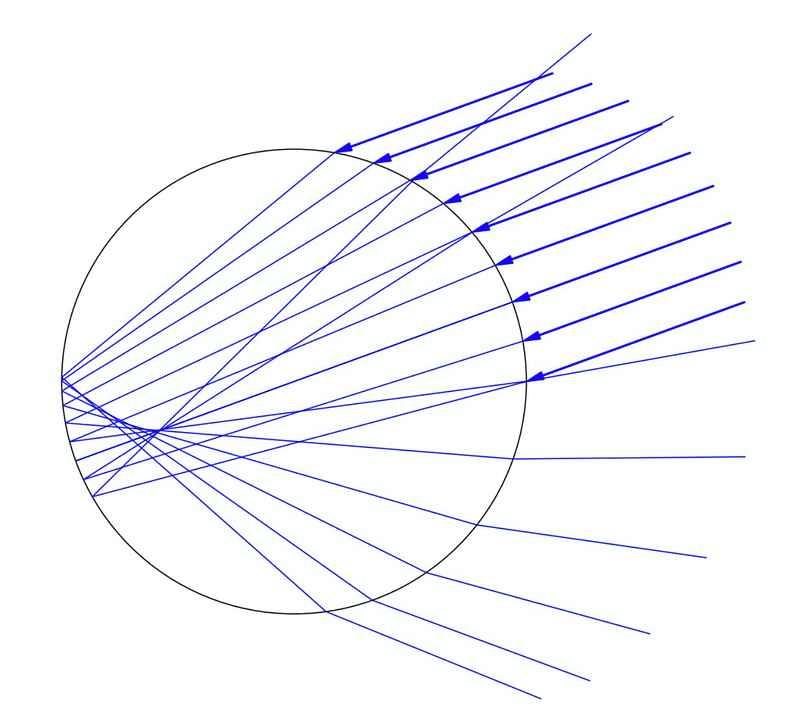
If the sun rises higher, say at 50°, the situation dramatically changes, with no rays directed toward the observer:
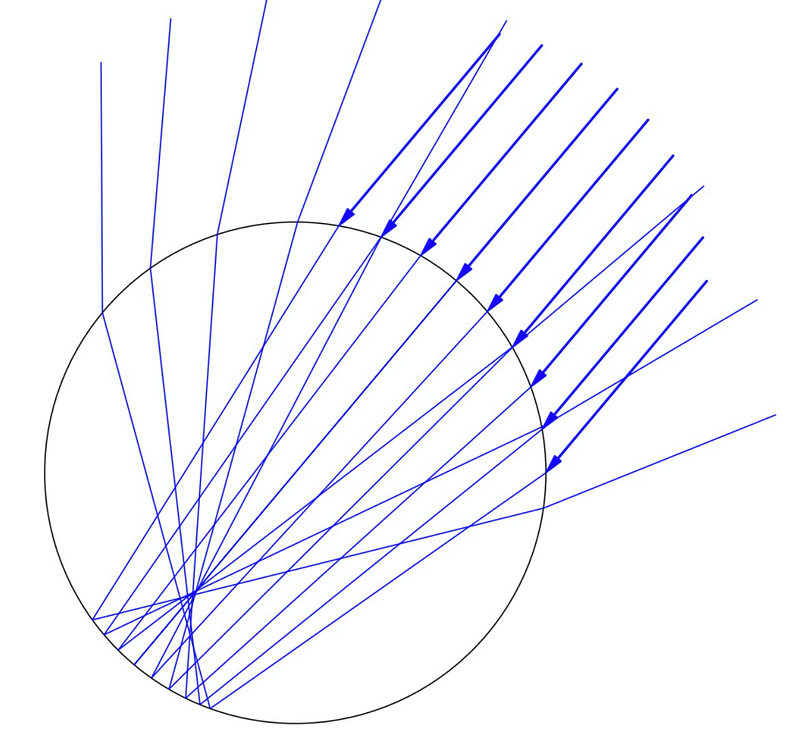
To conclude, we will also explore the potential for rainbows on Titan. Given that the refractive index of ammonia differs from water, we can see that the conditions for witnessing a rainbow on Titan are quite rare: